
United Kingdom, Feb 28, 2024
Zero Trust may be seen to some as just another framework for their organisation to spend precious time on. However, discount it at your peril, as implementing a well-defined Zero Trust can be one of the most effective tools in protecting your organisation and saving you money in the long run. Fundamentally, it sets organisations up for cyber resilience, supports your Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery plans and ensures you're prepared for an inevitable cyber breach.
That said, you may need to focus on achieving compliance with a specific regulation before moving onto Zero Trust. Will it align with other regulations, or will it require a whole new approach? The good news is, Zero Trust strategies align quite nicely with security standards and legislation, as it is fundamentally based on best practices and leverages the requirements which other regulations stipulate, such as NIS 2018. Therefore, implementing a Zero Trust strategy enables you to meet, or even exceed, a large section of other standards and regulatory requirements.
The compliance landscape is evolving rapidly, constantly developing and changing in scope, affecting more and more organisations of all sizes. Therefore, any opportunity to map overlapping requirements to save time and money should be explored. In addition, being in breach of one set of regulations can mean breaching multiple, increasing the risk of being fined from multiple regulatory bodies. Additionally, CISO’ are voicing real concern for now being personally liable for cyber-attacks, both criminally and financially. So, the need for implementing a Zero Trust strategy that overlaps with many critical compliance frameworks and legislation couldn’t be higher.
Let’s take a closer look with which common regulations and frameworks align with Zero Trust.
GDPR
GDPR protects data subjects and their confidential information, whilst Zero Trust assumes that a breach has already occurred in the first place. Combining the two, sets you up for supporting the requirements of GDPR. Putting an example into perspective, let’s say a data breach was to occur.
The ICO (Information Commissioner’s Office) provide guidance on how to manage a data breach which involves recording all information related to the incident. Zero Trust assumes a breach has occurred in the first place, supporting GDPR requirements and preventing these scenarios from happening in the first place. Furthermore, Zero Trust leverages the least privilege principle, so anyone who wishes to access certain data cannot do so. Continuous monitoring and authentication of users is another key requirement and this is where Zero Trust ties in nicely with GDPR. Zero Trust focuses on reducing the attack surface, meaning that potential threats have less entry points into an organisation’s network. Combining the two sets you up for increased compliance with GDPR and a stronger security landscape.
PCI DSS
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) addresses data breaches and how to prevent them, aligning well to Zero Trust, which assumes that a breach has already occurred, something which is not assumed in PCI.
PCI DSS also addresses the cost reduction of data breaches. When you combine this, with the correct Zero Trust implementation, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of a data breach occurring. PCI DSS further aligns with Zero Trust as it provides security controls that address network segmentation and continuous monitoring. There is a large focus on building and maintaining secure networks and systems, to handle payment card information securely, and preventing fraudulent actions. Lastly, reducing the network perimeter promoted by Zero Trust reduces access to cardholder data, signifying the importance of how they would both work together.
CIS
The Centre for Internet Security guidelines and controls look at prevention, detection, and response to cyber security threats, while Zero Trust looks at trusting nothing and verifying identities. When combining CIS with Zero Trust, it assists organisations in having a completely proactive approach to security. CIS controls, enforce additional layers of security through network segmentation, authentication methods and dynamic policy enforcement, which tie in nicely with Zero Trust principles. Therefore, combining both CIS guidelines and Zero Trust principles promotes an all-rounded approach to security.
NIST Special Publication (SP) 800-53 Framework
NIST promotes a risk-based approach, with several frameworks belonging to NIST supporting the same approach.
Firstly, there’s NIST SP 800-53 which has a focus on confidentiality, integrity, and security of federal information systems. NIST SP 800-53 provides the controls for multiple frameworks, designed to shape that risk-based approach. It supports NIST SP 800-37 Risk Management Framework (RMF) and is used in combination with NIST SP 800-207 which is NIST’s Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) Framework. This framework focuses on the logical components and focuses on protecting resources rather than network segments. The controls from NIST SP 800-53 are often used with NIST SP 800-207, highlighting the compatibility between these frameworks.
NIST SP 800-53 is flexible and can be used with multiple frameworks, including their own ZTA framework, so if you already use NIST SP 800-53, you’re in a good place to bring Zero Trust into the picture. All these frameworks create a solid foundation for a strong security posture and a comprehensive approach to safeguarding information systems and building a ZTA.
With evolving security threats in the cybersecurity landscape and many standards and regulations to comply with, implementing a Zero Trust strategy promotes best security practices and puts organisations in a good position to achieve other important standards. Zero Trust supports multiple regulations, so aligning with those regulations would put your organisation in the best position to exceed regulatory requirements and successfully implement a Zero Trust strategy.
If you are interested in implementing a Zero Trust strategy, where to start and what it could do for your organisation, Logicalis can help you.
Related Insights

United Kingdom , Feb 16, 2026
Q&A with Mike Fry: Tackling the Cybersecurity Skills Gap
To accompany the release of the recent IDC infographic “From Shortage to Strength: Fixing the Cyber Skills Gap,” we sat down with Mike Fry, Infrastructure, Data and Security Solutions Director at Logicalis UK&I, to get his view on the findings and what they mean for organisations today.

United Kingdom , Feb 9, 2026
The hidden dangers of AI: What we need to know now
Artificial Intelligence is popping up everywhere - from the apps we use every day to the tools shaping how businesses operate behind the scenes. It’s exciting, fast moving and packed with potential, but it also comes with risks that are becoming harder to ignore.

United Kingdom , Feb 5, 2026
Next-Generation Connectivity: The top 10 questions answered
In an era where a Teams call is more common than an in-person meeting, it has never been more crucial to comprehend the underlying technology that keeps our businesses connected: the network.

United Kingdom , Feb 4, 2026
Setting sail on your FinOps journey
FinOps offers a structured approach to optimise cloud infrastructure costs, foster strategic agility and cultural change. Logicalis provides a managed service model to help businesses adopt FinOps principles regardless of their cloud maturity.

United Kingdom , Jan 20, 2026
Why Now Is the Moment to Rethink Your Cisco Licensing Strategy
Budget pressures are rising. Security expectations are tightening, and digital transformation isn't slowing down. With many enterprises still managing Cisco software manually, can you unlock the agility your business needs quickly?

United Kingdom , Jan 9, 2026
Cybersecurity burnout
The cybersecurity landscape is evolving rapidly, demanding constant vigilance from already overstretched teams. As attacks rise in both scale and sophistication, many organisations are discovering a quieter yet equally dangerous threat from within: burnout.

United Kingdom , Jan 2, 2026
New Year, New Mindset: Security resolutions for 2026
Cybersecurity lessons from 2025 and practical steps to improve the security posture in 2026: focus on meaningful data outcomes, maintaining basic security practices, and proactive risk management to enhance resilience and operational effectiveness.

United Kingdom , Dec 19, 2025
Getting the best bang for your Cloud bucks: Reallocating cloud spend
Organisations are under increasing pressure to optimise cloud investments not only for financial returns but also for sustainability and operational value. As a result here's an active shift in how how spend is viewed.

Ireland , Dec 19, 2025
Digital by 2030
Ireland aims to deliver 90% of key public services digitally by 2030, focusing on trust, compliance, and citizen value while overcoming legacy system challenges. This roadmap guides IT leaders in secure and responsible modernisation without service disruption.

United Kingdom , Dec 18, 2025
Unifying fragmented defences to form Intelligent Security Operations
Modern cybersecurity challenges require unified intelligence to protect complex digital ecosystems. SIEM systems, like Microsoft Sentinel, are essential for enabling proactive threat detection and response.

United Kingdom , Dec 16, 2025
IBM acquires Confluent: What it means for the industry and for customers
IBM’s acquisition of Confluent for approximately $11 billion marks a significant development in data streaming and AI-driven enterprise innovation.

Ireland , Dec 15, 2025
A practical guide to AI automation for businesses
Artificial Intelligence has become essential for modern business operations, enhancing productivity, streamlining processes, and enabling scalable solutions through Microsoft's AI ecosystem. This guide outlines a three-step approach to leveraging AI effectively in organisations.

United Kingdom , Dec 12, 2025
Building Connectivity for agility and innovation
Intelligent Connectivity offers a future-ready network that is agile, scalable, and designed to support continuous innovation and sustainability. It addresses challenges like vendor lock-in and complex licensing.

United Kingdom , Dec 9, 2025
Responsible AI starts here
Artificial Intelligence is becoming a critical priority for organisations in the UK and Ireland. Microsoft Purview and Copilot together enable responsible AI adoption by ensuring data security and enhancing productivity within applications.

United Kingdom , Dec 4, 2025
Cloud costs are on the rise, and strategic oversight is more critical than ever before
Cloud computing offers agility and innovation but has led to rapidly rising infrastructure costs, with cloud spending projected to dominate IT budgets by 2029 and increasing nearly 100% year-over-year in late 2024.

United Kingdom , Dec 1, 2025
Taking a new approach to your network
Logicalis and Extreme Networks offer Intelligent Connectivity, a managed network service designed to provide businesses with a unified, flexible, and secure solution that adapts to growth and change while simplifying management and enhancing security.

United Kingdom , Nov 28, 2025
Bringing sustainability to life
The Logicalis Volunteer Day Scheme allows employees to take a day off for charitable work, with a new focus on environmental conservation and carbon offsetting across UK, Ireland, and Channel Islands.

United Kingdom , Nov 11, 2025
Cybersecurity at a Crossroads
The Microsoft Digital Defence Report 2025 and the Logicalis CIO Report 2025 both highlight the critical evolution of cybersecurity from a technical issue to a core business imperative that requires board-level attention and strategic alignment.

United Kingdom , Nov 5, 2025
The power of Responsible Business
Customers, partners, investors, and employees are all looking for organisations that not only deliver results but do so with integrity, transparency, and a genuine commitment to making a positive impact.

United Kingdom , Nov 3, 2025
Why does your network need to evolve?
The number of challenges faced by legacy networks is rising, emphasising the need for agile, secure, and observable networks. Intelligent Connectivity by Logicalis powered by Extreme Networks as a future-focused solution can help.

United Kingdom , Oct 30, 2025
Private 5G: Is the Utilities sector ready to power up?
Private 5G offers the utilities sector enhanced security, low latency, and automated capabilities that can improve operational efficiency and resilience while maintaining regulatory compliance.

United Kingdom , Oct 24, 2025
Lessons learned from this week's AWS outage
The AWS outage on October 20, 2025, caused by a DNS failure in the US-EAST-1 region, had a widespread impact on services and businesses. Another highlight of the importance of resilience in cloud architectures, Logicalis offers guidance on preparing for future disruptions.

United Kingdom , Oct 16, 2025
The wireless wake-up call for CIOs
Research reveals that CIOs in the UK, Ireland, and Channel Islands lag behind global peers in adopting IoT and Private 5G technologies despite budget allocations for these investments. Addressing barriers like budget, compliance, and skills is crucial for closing this gap and unlocking competitive advantages.
United Kingdom , Jul 11, 2025
The Game-Changer our customers didn't know they needed
As a Solutions Architect working with organisations across a multitude of sectors, from Education and Government to manufacturing, transport and retail, we get a front-row seat to the evolving challenges that senior IT and business leaders face.

United Kingdom , Jun 30, 2025
Blog, Videos
Steering the Carbon Conversation
Sustainability has moved from a corporate ambition to a strategic necessity. But unlocking real impact depends on how effectively organisations can harness their ESG data to drive decisions, meet compliance obligations, and future-proof operations.

Jersey , Jun 26, 2025
Championing the future Leaders of Technology
Logicalis recently presented the Excellence in IT Award at Highlands College for the 5th year running, reaffirming our commitment to fostering the next generation of IT talent.

United Kingdom , Jun 12, 2025
IBM Turbonomic: AI-driven IT Automation to Slash Infrastructure Costs
In a landscape where IT performance must meet tight budgets and rapid innovation, IBM Turbonomic stands out by combining artificial intelligence with intelligent automation to optimise resources and reduce IT spend while maintaining service quality.

United Kingdom , Jun 6, 2025
MXDR is the advantage the C-Suite need for assured cyber resilience
Cybersecurity isn’t just an IT problem. It’s a boardroom issue and one that has regulatory, financial and reputational consequences. With frameworks such as the DORA and NIS2, which is relevant to many UK organisations, as they trade in the EU.

United Kingdom , Jun 6, 2025
AI that works for you in the age of watsonx
AI is past the hype and becoming part of the norm, offering businesses new opportunities to innovate and stay ahead. However, organisations face a key challenge—whether to build AI solutions for greater control or buy ready-made solutions for faster results.

United Kingdom , Jun 3, 2025
AI Agents and the Future of Data-Driven Innovation
Welcome to the first in a series of blogs that explores all things Data and AI, and explore the rise of AI agents, the concept of Agentic AI, and introduce the Model Context Protocol (MCP) a game-changer set to redefine how we collaborate and deliver value through technology.

United Kingdom , May 20, 2025
Unifying automated security to overcome IT middle management challenges
In today’s fast-evolving digital world, cyber threats are more sophisticated and harder to detect. IT security teams face increasing pressure to protect complex environments with limited resources and fragmented tools.

United Kingdom , May 19, 2025
Behind the delegate pass of IBM THINK 2025
At THINK 2025, IBM didn’t just unveil new technologies; it reframed the enterprise AI conversation. For CIOs, the message was unmistakable: the age of AI pilots and proof-of-concepts is over. The next wave is about operationalising AI at scale.

United Kingdom , Apr 30, 2025
How to make your tech investment deliver business benefits
According to our Logicalis 2025 CIO Report these same executives are no longer just technology implementers—they've become strategic architects of business direction, with 94% confirming their expanding role in shaping company strategy.

United Kingdom , Apr 10, 2025
From bottlenecks to breakthroughs: How Private 5G is transforming port operations
Unlike Public 5G, Private 5G gives businesses full control over their networks, allowing them to customise their connectivity for mission-critical applications, while tightening any necessary security measures.

United Kingdom , Mar 27, 2025
How does Microsoft 365 Copilot leverage AI to maximise your team's productivity?
How Can Microsoft Copilot AI Capabilities Maximise Your Productivity? You may be using Microsoft Copilot AI, but are you making full use of it? Discover how to make the most out of Copilot to maximise your team’s productivity.

United Kingdom , Mar 27, 2025
Logicalis and NetApp: Strengthen your Cyber Resilience with Secure SAN
Cyberattacks are surging, rising 30% in 2024 alone. Over 70% of UKI companies have already experienced a breach, and in the US, the average data breach cost has jumped to nearly $4 million. If you think it won’t happen to you, think again. It’s not a question of 'if’ but ‘when’.

United Kingdom , Feb 26, 2025
Blog
Behind the delegate pass of Cisco Live 2025
Let me take you behind the scenes of what was an incredible week at Cisco Live Amsterdam 2025. As someone who was there on the ground, I wanted to share the innovations that got everyone talking – and more importantly, what they mean for your business.

United Kingdom , Dec 4, 2024
Microsoft Ignite 2024: Copilot innovation and advancements in security
The major announcements highlighted this year focused on Copilot and Security. While this may not come as a surprise, everyone should be excited about what these advancements mean for the upcoming year.

United Kingdom , Nov 7, 2024
Logicalis renews Microsoft Global Azure Expert MSP status
Logicalis are proud to announce they have renewed the prestigious Global Azure Expert Managed Service Provider (AEMSP) certification. This accolade not only showcases Logicalis’ in-depth knowledge and proficiency in deploying, managing, and optimising Azure-based solutions but also emphasises their ability to deliver transformative outcomes for clients.

United Kingdom , Nov 5, 2024
Logicalis UK&I named supplier on G-Cloud 14 Framework
Logicalis UKI, an international IT solutions and managed services provider, has been listed as a supplier on the G-Cloud 14 Cloud Services and Solutions Framework.

United Kingdom , Aug 27, 2024
Circular logic –Why IT leaders need to embrace circularity for sustainable IT
IT leaders have a unique opportunity to drive substantial reductions in their organisation's carbon footprint while also realising significant cost savings. In our 2024 CIO report, 93% of CIOs believe IT is core to successfully delivering on their organisation's environmental objectives.
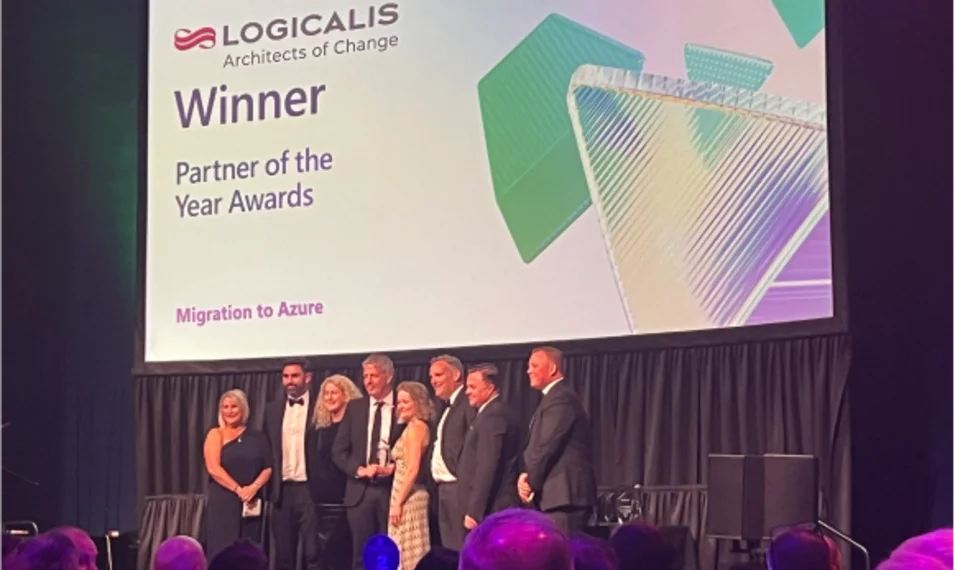

Ireland , Aug 21, 2024
Logicalis wins at Microsoft Ireland Partner of the Year Awards
Earlier this summer, we were proud to receive a 2024 Microsoft Ireland Partner of the Year award in the “Migration to Azure” category at Microsoft Ireland’s annual awards ceremony at the Mansion Room in Dublin. The Microsoft Ireland Partner of the Year Awards recognise and celebrate the achievements of and excellence within the company’s partner network.

United Kingdom , Jul 10, 2024
Embracing Change: An Approach to Cybersecurity in Today's Digital Landscape
Let's talk about change. At Logicalis, change isn't just a buzzword; it's a reality we've embraced wholeheartedly. Why? Because we understand that the world around us is constantly evolving, especially when it comes to how we work.

United Kingdom , Jul 1, 2024
Top Five Business Considerations for NIS2 Compliance
With the forthcoming enforcement of the NIS2 directive on October 18, 2024, businesses across the EU must prepare for a new era in cybersecurity compliance. Here, we explore the top five business considerations to help you navigate this critical regulatory shift and ensure your organisation is ready.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
IBM Power Platforms for High-Performance Computing Workloads
High-performance computing (HPC) is a critical component in the fields of scientific and engineering research, financial modelling, artificial intelligence (AI), and more. IBM Power platforms have emerged as a formidable player in this arena. This Q&A op-ed explores why IBM Power is an exciting option for HPC challenges, its role in sustainable IT, and its advantages for AI applications.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
IBM Turbonomic: Embracing AI in Automating IT Operations and Reducing IT Spend
As companies digitise and expand their IT infrastructure, the demand for smart, automated solutions like IBM Turbonomic will increase. This platform offers valuable insights and automates complex IT tasks, making it essential for modern businesses.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
IBM Envizi ESG Reporting and Scope 3 Emissions Management
Businesses recognise the importance of sustainability and environmental responsibility. To meet their ESG responsibilities, companies are turning to IBM Envizi, a software suite that simplifies ESG reporting and manages Scope 3 emissions. See why.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
Q&A on IBM Envizi: Driving Sustainability with Precision
IBM Envizi offers a powerful solution for organisations looking to enhance their ESG management enabling Chief Sustainability Officers to make informed decisions, ensure compliance, and improve stakeholder trust.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
Leverage the transformative power of IBM's watsonx portfolio
Read about IBM's watsonx AI portfolio and its transformative potential for organisations of all sizes.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2024
IBM THINK 2024: Key announcements
Read the latest key announcements delivered at IBM THINK 2024, highlighting IBM's ongoing innovations and partnerships across AI, hybrid cloud, quantum computing and more.

United Kingdom , Jun 27, 2024
Green Operations: Pioneering Sustainable IT with IBM Turbonomic and the Future of IBM's Automation Software Portfolio
The future of cloud computing lies in its ability to balance technological advancement with environmental responsibility. See how IBM’s comprehensive automation portfolio is poised for a greener, more sustainable future.

United Kingdom , Jun 27, 2024
Maximising ITAM with Flexera: Enhancing Operational Effectiveness, Resilience, and Compliance
If your organisation is looking to optimise its software asset management, improve operational efficiency, and ensure compliance, Flexera stands out as a vital tool in the digital age.

United Kingdom , Jun 27, 2024
Harnessing the Power of IBM Apptio to Reduce Cloud Costs: A Strategic Imperative for CFOs
As the adoption of hybrid IT environments continues to grow, the importance of a robust ITFM solution like IBM Apptio cannot be overstated.

United Kingdom , Jun 24, 2024
Understanding NIS2: The Next Evolution in EU Cybersecurity Legislation
In the realm of cybersecurity, evolution is not just inevitable; it is essential. One significant development in the European Union (EU) is the introduction of the NIS2 directive. This blog delves into the journey from NIS to NIS2, highlighting its enhanced requirements, expanded industry scope, and the implications for businesses across the EU.

United Kingdom , May 6, 2024
Getting your house in order: how an IT infrastructure review can inform your data storage decisions
Data storage costs vital resources. Get your house in order with a professional IT infrastructure review, and save significantly on your running costs.
United Kingdom , Apr 29, 2024
How CIOs can navigate new cybersecurity threats posed by Gen AI and quantum computing
If the last year showed us anything, it’s that we have ventured into a completely new age of technology. AI and quantum computing have developed quickly and, understandably, business leaders are keen to jump in and start utilising them to propel their business goals, across every sector. Get on the front-foot and find out more.

United Kingdom , Apr 29, 2024
How CIOs can overcome gaps in skills, security and compliance to deliver successful digital transformation projects
Digital transformations are tricky. They often start off so well but then often snowball and become increasingly complicated and costly. But why, and what is causing these costs to rocket and deadlines to be delayed?

United Kingdom , Apr 29, 2024
The carbon footprint of data storage: How to modernise for the future and make your business more sustainable
The carbon footprint of data storage is an issue that businesses need to address. Reduce your data storage carbon footprint with Logicalis and NetApp.

United Kingdom , Apr 22, 2024
How hybrid flash data storage can support your journey towards a green data centre
If you want to run a green data centre, you’ll need an efficient data storage solution to help you. NetApp hybrid flash data storage offers the benefits of both hybrid cloud data storage and flash technology.

United Kingdom , Apr 15, 2024
Modern data storage technologies and how they can support your business to simplify, sustain and grow
Cloud ready, flexible flash storage that’s secure and sustainable. Discover how modern data storage technologies can help you simplify, sustain and grow.

United Kingdom , Mar 21, 2024
Exploring Highlights from Cisco Live 2024
Reflecting on the insightful happenings of Cisco Live 2024 in Amsterdam, I wanted to further delve into the key takeaways from this event.

United Kingdom , Mar 6, 2024
A decade of insight reveals the future of tech leadership in the Logicalis Global CIO Report 2024
In the ever-changing landscape of tech leadership, we like to think of the Logicalis CIO Report as a steadfast guide, reflecting the pulse of change in the industry. As we celebrate the 10th Anniversary of this ground-breaking report we hope it continues to serve as a roadmap to the future, a visionary lens to what lies ahead.

United Kingdom , Feb 14, 2024
Unlocking the Future: A recap of Cisco Live EMEA 2024
Cisco Live EMEA, the pinnacle event for technology enthusiasts in Europe, recently concluded with a flurry of announcements and insights that have left the IT community buzzing. Explore our Cisco Live recap, as we explore the implications of these ground-breaking announcements.

United Kingdom , Jan 23, 2024
Zero Trust – Six Steps to Success
Zero Trust; those buzzwords that you keep hearing about, and you’ve seen the importance of it all. But how do you really begin your Zero Trust journey? Are you even ready for Zero Trust? Follow our Six Steps to Success for your company to move forward in the world of security.

United Kingdom , Jan 17, 2024
Latest EOX Announcements from Cisco
EOX is a critical milestone when looking at the lifecycle of your Cisco environment. Logicalis have compiled the latest Cisco announcements into an easy-to-navigate report that allows you to obtain end-of-life information including the latest End of Sale announcements and all products which are going End of Life, End of Attach and End of Security Vulnerability.

United Kingdom , Jan 8, 2024
Smart Buildings and Campus Connectivity
Create a more intelligent, more efficient building that better serves the needs of your growing business.

United Kingdom , Dec 21, 2023
Cyber Resilience – don’t play to win, play not to lose
Tyson Fury is considered by many to be one of the greatest boxers of our time. It is an interesting observation that on the surface, seems implausible when you consider that he does not appear to be the most muscular, the leanest of the fittest fighter out there. He is of course, not infallible. On many occasions, despite his size, he has been knocked off his by feet by fighters seemingly smaller and weaker.

United Kingdom , Dec 21, 2023
The carbon footprint conundrum and how your company can tackle it
The rising pressure from stakeholders. The heightened reporting requirements. The influence on the buying process. The competitive advantage for companies with a lower carbon footprint. There are many reasons that sustainability is front of mind for businesses. In fact, these days you’re in the minority if it’s not on your organisation’s priority list.

United Kingdom , Dec 21, 2023
Placing your faith in AI – how it can benefit your cybersecurity strategy
2023 will always be remembered as the year in which the progress and capability of Artificial Intelligence (AI) truly accelerated. Following the launch of ChatGPT in late-2022, the technology and its various capabilities have moved from a science fiction concept in most people’s minds to an everyday reality.

United Kingdom , Dec 14, 2023
How CIOs can secure and optimise Cloud with Logicalis
In 2023 Microsoft Azure grew its market share by 24%, twice the rate of its nearest rival AWS. The growth in complexity and market share is creating a worldwide shortage of people with the skills to optimise it. Logicalis can identify and relieve the pressure points and help you to obtain that peace of mind.

United Kingdom , Dec 12, 2023
Zero Trust – Is it all just hype?
Zero Trust is everywhere. Seemingly replacing ‘Digital Transformation’, it has rapidly become the new darling of the marketing word of our time. Yet beneath the marketing veneer, it has a fundamental message that everyone should take note of; it will help protect your organisation, your people and your reputation.

United Kingdom , Dec 12, 2023
Achieve your sustainability goals with Logicalis
Sustainability has gone from being a “nice to have” to a key factor when making strategic IT decisions, and we at Logicalis are ready to help our customers achieve their sustainability goals.

United Kingdom , Dec 12, 2023
Zero Trust - The 3 Guiding Principles
So, what is Zero Trust? Remember, it’s not a product – it’s a strategy that’s implemented through people, process, and technology.

United Kingdom , Nov 13, 2023
Logicalis named 2023 Cisco Global Enterprise Networking and Meraki Partner of the Year for the second consecutive year
Last week, we proudly received the 2023 Cisco Global Enterprise Networking and Meraki Partner of the Year award during Cisco’s annual Partner Summit. The award recognised Logicalis' global capability in Enterprise networking, with Logicalis Portugal receiving a special mention for their standout contribution to driving Intelligent Connectivity managed services to customers in Portugal.

Australia , Oct 24, 2023
Choosing the right MSSP -Top 5 credentials to look for when selecting a MSSP
In an increasingly interconnected world, the frequency and complexity of cybersecurity threats are rising.

United Kingdom , Sep 22, 2023
Cisco Prime Reaches End of Life (EOL): What's Next?
In the world of networking, Cisco Prime Infrastructure has been an essential tool for many professionals. On March 31 2023, Cisco announced the End of Life (EOL) for Cisco Prime. Now is the time to start your migration to ensure a seamless transition to the new platform.

United Kingdom , Sep 18, 2023
Unlocking IT Transformation Success with Cross-Functional Value Stream Teams
Today, we're diving into an exciting topic that's reshaping the world of IT transformation: cross-functional value stream teams. Imagine a world where IT projects not only meet but exceed expectations, all while staying on budget and on schedule. It might sound like a dream, but Logicalis is here to show you how it can become your reality.

United Kingdom , Sep 18, 2023
Driving Sustainability with Technology Lifecycle Management
Sustainability has become a critical issue for businesses across the globe, and the IT industry is no exception. With increasing awareness of environmental impact, organisations are now looking to adopt sustainable IT practices that minimise their negative impact on the environment. Sustainable IT aims to reduce the environmental footprint of all areas of IT operations, from the purchasing, usage and disposal of IT assets to the energy consumption of IT equipment.

United Kingdom , Sep 4, 2023
Logicalis expand their suite of Cisco-powered managed services with the launch of Intelligent Connectivity
Logicalis, a global technology service provider, delivering next-generation digital managed services, has announced the launch of Intelligent Connectivity powered by Cisco, a suite of solutions including Private 5G, SD-WAN, SASE, SSE, SD-Access and ACI Data Centre.

United Kingdom , Aug 15, 2023
Don’t let the tech skills gap slow you down
As many of us know, the technology and IT sectors are booming and experiencing rapid innovation. Add to this the growing lack of available talent, and IT leaders are finding themselves struggling to keep pace with constantly changing technology.

United Kingdom , Jul 28, 2023
Keeping your Microsoft environment up to date with Unified Microsoft Updates
Keeping your IT environment secure and up to date is a challenge that requires a reliable and efficient solution. Microsoft offers Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) as an on-premises role that lets you download and distribute updates for Windows and other Microsoft products to your network computers. Logicalis can collaborate with you in the aim to streamline your digital environment's operation and management.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2023
IT professionals required to do more with less as security threats remain major concern
IT security remains a top priority for most UK&I IT professionals as revealed by Logicalis’ 2023 IT Survey Results. The survey finds 71% of IT professionals list security as their top priority for the year. The independent UK and Ireland survey, which canvassed the opinions of over 1000 IT professionals from across the UK&I, unveils businesses are grappling with tightening IT budgets, changing IT priorities, and elevated concerns over security threats and technical skills shortages.

United Kingdom , Jun 15, 2023
Secure your end-of-life servers with virtual patching
Unfortunately, the longer you work in cybersecurity, the more often you come across legacy operating systems and applications. These types of technologies can be a nightmare to manage and represent a huge security gap for your organisation. On 10th October 2023, Microsoft will end support for Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2, meaning no more security updates will be available, just like SQL Server 2012.

United Kingdom , May 30, 2023
Join Logicalis at CIO & IT Leaders Summit 7th June 2023, Croke Park, Dublin
Logicalis, in partnership with IBM, is delighted to be supporting this year’s CIO & IT Leaders Summit, Optimising technology assets to drive real value, in Croke Park, Dublin, 7th June 2023. With many valued customers across the UK and Ireland community, we look forward to welcoming you to the event.

United Kingdom , May 25, 2023
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE)
There are a number of software licencing issues with Cisco’s ISE platform that we are keen to make customers aware of. If you are running a 2.x version of ISE, then this has an ‘End of Life’ announcement, and you need to act now. Read now for more detail around your options.

United Kingdom , May 25, 2023
Latest EOX Announcements from Cisco
EOX is a critical milestone when looking at the lifecycle of your Cisco environment and often prompts organisations to review the impact of EOX to products, services, or subscriptions. Logicalis have compiled the latest Cisco announcements into an easy-to-read report that allows you to obtain end-of-life information including the latest End of Sale announcements and all products which are going End of Life, End of Attach and End of Security Vulnerability.
United Kingdom , May 2, 2023
Ensure critical performance and reduce network complexity with Logicalis Network Managed Services
At a time when customers are increasingly looking to move from capital expenditure (CapEx) to operational expenditure (OpEx) many areas of IT have seen dramatic changes. We are fully committed to providing world class networking solutions to our customers with a suite of expert service offerings that enable customers to scale their network with better predictability and cost-effectiveness.
United Kingdom , Apr 6, 2023
Introducing our Managed Digital Fabric Platform
When I talk to my peers across the industry, many CIOs face budget constraints, making it essential to do more with less. They are also being asked to help the business realise new revenue streams with technology and looking to accelerate their digital transformation plans. But with complex layers of digital infrastructure, how can they see the bigger picture and take the right action? Our Logicalis CIO study of 1,000 global CIOs found that 75% need help to unlock their data to drive successful transformation

United Kingdom , Mar 31, 2023
How CIOs are building resilience with digital managed services
If the last few years have taught us anything, it is that life is unpredictable. This perma-crisis of unpredictability is set to continue as we have conflicts, financial instability, and increasing natural disasters. So while CIOs are helping organisations to innovate at pace and scale, it’s never been more important to balance that momentum with risk awareness and resilience. In 2023, the role of the CIO must be to enhance existing capabilities and create new ones, while protecting the organisation from continued volatility and increased risk.

United Kingdom , Mar 31, 2023
Three ways CIOs are driving the transition to net zero
The transition to net zero offers a great opportunity for CIO’s to increase their strategic influence in their organisations. Tech leaders are in an ideal position to advance sustainability by driving digital transformation, improving energy efficiency, and reducing carbon emissions.

Ireland , Mar 21, 2023
Observability: Bridging Business, Customers and User Experience
Last month, we hosted an Observability event in Dublin with our Ireland customers. Held at the world-renowned Teeling Whiskey Distillery, which proved a great backdrop for sharing engaging content and entertaining conversation, we explored the importance of observability. For those who were unable to attend, or are unfamiliar with the term 'Observability', we have provided you with our 5 Key Takeaways from the event, and how digital-first enterprises can address the increased complexity brought by modern IT architectures.

United Kingdom , Feb 7, 2023
Have we found the modern-day Pandora’s box?
So unless you have been hiding in a cave or living under a large rock, you will have heard of ChatGPT - the revolutionary AI that has taken the world by storm. In its first five days, it managed to amass 1M users and looking ahead it is projected to be able to achieve revenues of $1B by the end of 2024. That is seriously impressive - and technology like this doesn’t come along very often. But what is going to be the impact on the world of this new AI and have we opened a modern-day Pandora’s Box?

United Kingdom , Jan 27, 2023
Logicalis CTO Toby Alcock highlights enterprise tech trends for 2023
At Logicalis, as we look forward to yet another busy and challenging year for the IT industry, we've put together the strategic technology trends for 2023 that can help IT leaders see through the current economic and market challenges and deliver sustainable business outcomes that matter.

United Kingdom , Jan 25, 2023
Challenges & Benefits of Security Information & Event Management (SIEM) Adoption
Traditional SIEM solutions were deployed on premises, needing competency in sizing, scoping and considerable resources to run. Next generation SIEM solutions are Software as a Service (SaaS) based in the cloud, taking out a lot of the upfront pain at the design stage and allowing for ‘scale up’ of the platform, as the enterprise grows. Overcome the challenges to achieve SIEM success.

United Kingdom , Jan 20, 2023
What does remediation mean to you?
Get to grips with remediation and understand what it means in a business context. An EDR solution may offer remediation actions as part of its set of capabilities. But to what extent? Which teams are involved in the delivery and management of that, and where do you go if you still have questions or need advice to progress your journey towards an increased security posture?

United Kingdom , Jan 11, 2023
Announcing End of Extended Security Updates and Support for Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2
Are you still running Windows Server 2008 R2? With Windows Server 2008 R2 reaching the end of its Extended Security Update on January 10th, it is highly recommended that you take the time to assess your current infrastructure to ensure that your organisation can continue to operate securely and efficiently.

United Kingdom , Dec 5, 2022
Do managed service providers hold the answers to a sustainable future in IT?
With sustainability top of mind for everyone, organisations are demanding transparency and clarity from suppliers and partners around ESG goals today. It’s clear that businesses expect the organisations they engage with to do more to offset their environmental impact. For example, data from 2018 showed that 62 per cent of consumers wanted companies to take a stand on issues including sustainability, transparency, and fair employment; in 2022, that number has grown to 72 per cent.

United Kingdom , Nov 29, 2022
Key Takeaways from VMware Explore
So it has been 2 weeks since I attended VMware Explore in Barcelona and looking back there were a number of key announcements that were made at the event. Firstly, it was great to see so many people at an event after the last few years and also being from the rainy north of England, it was great to enjoy a little Spanish sunshine whilst taking in the learnings from the three days.

United Kingdom , Nov 23, 2022
How to Continue Transforming During a Recession
With the current economic slowdown, it looks like another recession could be on the cards in 2023. This usually heralds a period of consolidation within IT and the closing of the purse strings with regards to planned investments. In previous decades this was standard practice, but now that we’re in a digital age, many businesses can’t afford to slow down their digital transformations if they want to survive.

United Kingdom , Nov 23, 2022
Reducing Digital Waste
Sustainability is imperative to all our futures and is directly impacted by every device we use that consumes power. This includes the on-premises and cloud infrastructures that power our digital work lives. To be as sustainable as possible we need to ensure that we are consuming the least amount of infrastructure to host our workloads and services, without impacting their availability, performance or governance.

United Kingdom , Nov 9, 2022
How Digital Managed Services are driving business value for CIOs
Today’s CIOs face key challenges around futureproofing, innovating, and the perennial skills shortage. As businesses increasingly adopt a digital-first approach, CIOs need to deliver solutions and services that are future-ready, not stuck in the past, to mitigate the risks of these challenges. For many businesses, this means it’s time to invest in products and partners that align with your vision for what’s next, and that are able and willing to help futureproof your organisation.

United Kingdom , Nov 7, 2022
Take advantage of limited-time IBM price promotions on a range of IBM rack servers and storage systems
In partnership with IBM, Logicalis is delighted to announce a series of price promotions, covering a range of IBM rack servers and storage systems.

United Kingdom , Oct 27, 2022
Time to move from reactive to proactive protection against modern cyber attacks
As new cyberattack threats continue to emerge, organisations need to think differently about how they are securing their vital data, systems, and infrastructure.

United Kingdom , Oct 26, 2022
Why single-vendor vertical stacks still matter in a Hybrid Cloud world
As hybrid cloud becomes the IT architecture of choice, it is tempting to think the days of the single-vendor vertical stack are numbered.

United Kingdom , Oct 26, 2022
Hybrid Cloud and the pitfalls of DIY architecture
Before cloud, on-premise IT architectures tended to follow a DIY approach, piecing together best of breed offerings from different vendors - database from Oracle, storage from Netapp, compute from IBM, and so on.

United Kingdom , Oct 21, 2022
Reflections from our recent IBM Business Intelligence & Analytics event
I had the great pleasure last week attending and speaking at our joint Logicalis and IBM Business Intelligence & Analytics event in London, alongside some of IBM’s data and AI experts, Matthew Robinson and Louis Regan. From hearing about IBM’s future technology roadmap and how IBM tooling can deliver greater insights, it was the open conversations between customers and Logicalis and IBM experts that was truly insightful. Here are the key takeaways I learnt from the event:

United Kingdom , Oct 14, 2022
Confessions of a CEO: In a climate conscious world, does the train beat the plane?
More and more climate-conscious travellers are opting to take the train instead of flying. With this in mind, and a business meeting coming up in Cologne, I decided to take the 580km trip by train.

United Kingdom , Sep 26, 2022
Superhuman scale: What's possible with the next generation of digital managed services?
Business conditions have never been more volatile due to the cost-of-living crisis and subsequent economic shocks. How do businesses stay healthy amid inflationary worries, supply chain constraints, increasing security threats and skills shortages? The Logicalis 2021 CIO Survey found businesses are thinking outside the box. Technology decision-makers are planning to innovate their way through changing times over the next 12 months.

United Kingdom , Sep 23, 2022
Logicalis expands optimisation services in cloud cost management and Microsoft 365 environments
At a time when agility, security and resilience have never been more important, Logicalis has developed several expert service offerings that enable customers to automate cloud resource optimisation and maximise their Microsoft investment across their IT environments.

Ireland , Aug 23, 2022
Rethinking business as usual is the way to not only recover but thrive
It goes without saying that the pandemic permanently changed the way people work and how organisations operate. Hybrid working has become the norm and employee expectations have evolved – and will continue to do so – as people balance professional and personal responsibilities in a way that works for them.

Ireland , Aug 16, 2022
Innovation needs to be a priority post-pandemic
Business leaders need to redefine workstyles and empower people using the digital workplace as we move forward. Equipping people with optimised spaces, streamlined processes and cutting-edge technologies will support collaboration, innovation and productivity.

Ireland , Aug 10, 2022
How to secure your company in hybrid working times
The workplace of today is hybrid in many ways. Physical office space remains but is combined with remote working capabilities and virtual communications. There are those who work from home full-time and there are those who split their time across different locations. The hours people work vary greatly, as do the locations they work in.

United Kingdom , Jul 21, 2022
Oracle 12.1 Moves to Sustaining Support
Oracle users of Database version 12.1 will move from Extended Support to Sustaining Support at the end of July 2022, ending access to new security patches and bug fixes, which would inevitably leave the database less secure, and potentially at risk of tax, legal and regulatory non-compliance.

United Kingdom , Jul 5, 2022
Strong digital foundations are the key to enterprise agility
Hybrid working, an increase in cyber-attacks and a focus on sustainability have caused businesses to confront a big decision: transition into a digital-first business or face being left behind by the competition.

United Kingdom , Jun 28, 2022
Is IT complexity a significant factor in managing IT risk?
My emerging view of the key IT issue businesses are focusing on in 2022, is IT risk. It may be dressed up as something different, but fundamentally it is risk. This is caused by:

United Kingdom , Jun 27, 2022
Is it time for Business Process Management software to join the enterprise platform big league?
Business Process Management (BPM) has had something of a chequered history in the enterprise space. While Lean, Six Sigma and other quality methodologies have led some organisations to embrace formal process management as part of their DNA, others have not achieved the same level of traction.

United Kingdom , Jun 23, 2022
How to make the most of chatbots
Chatbots are all around us. Visit any eCommerce website today and the chances are it’ll instantly present you with a ‘How can I help you today?’ pop-up. The global market for intelligent virtual assistants is expected to grow at a CAGR of 28.5% from 2021 to 2028, and social media is full of amusing stories of parrots and small children wreaking havoc via Alexa.

United Kingdom , Jun 20, 2022
A brief guide to Business Process Management (BPM)
Effective Business Process Management (BPM) is an essential foundation for any successful business digitalisation and automation strategy. In summary, you can’t successfully automate a process unless you understand it fully, and BPM provides this understanding.

United Kingdom , Jun 10, 2022
Breaking down the great global data challenge
There are plenty of statistics around the staggering amount of data being created and consumed globally every day. 2.5 quintillion (million million million) bytes created daily by internet users, a 5000% increase in data interactions between 2010 and 2020, and so on.

United Kingdom , Jun 7, 2022
Information Lifecycle Management - Data is a business asset, so manage it
Data is a valuable business asset, yet many organizations are still not managing it with the same rigour they apply to physical assets.

United Kingdom , Jun 3, 2022
Explaining some important data management concepts and terms
Recent Logicalis UKI eBooks and articles have focused on the critical role of data in digital business, from unstructured data and the role of Information Lifecycle Management to the importance of robust, business-driven data storage strategy.

United Kingdom , Jun 1, 2022
How multi cloud data fabrics maximise data value
As data becomes an increasingly valuable asset, organisations have to adapt, to manage and protect their data to ensure it delivers maximum value to the business.

United Kingdom , May 30, 2022
Why data storage trends are about more than just technology
There are plenty of informative and valuable articles on the web about trends in data storage technology, discussing everything from reducing last byte latency to the wonders of consumption-based pricing. Data and storage are hot topics, unsurprisingly in an age where, as Mckinsey puts it, ‘“digital” and “data” have become the talk of the town.’

United Kingdom , May 25, 2022
Is it time to stop talking about the death of tape storage?
Heritage technologies - mainframe, Unix and magnetic tape in particular – have long been a rich source for the ‘is x technology dead?’ debate. Technical pundits fill the web with head scratching over why they haven’t disappeared, or defences for their survival.

United Kingdom , May 20, 2022
How to avoid the pitfalls of ‘good enough’ IT
In challenging economic times, organisations naturally look to cut back or defer non-essential investment. IT spend has traditionally been one of the areas businesses look to first when the need arises to cut budgets or delay projects, sometimes creating a ‘good enough IT’ mindset, where any IT asset that is doing the job reasonably effectively today is maintained beyond the last responsible moment for replacement.

United Kingdom , May 16, 2022
Should we stop being ageist about Unix?
"Unix is dead, long live Unix" – a headline that is still as topical today as it was in 2009, when a blog with that title was published to mark Unix’s 40th birthday.

United Kingdom , May 13, 2022
Where next for Virtualisation?
In its broadest sense, virtualisation can be seen as the progressive freeing up of any computing function – compute, storage, network – from the constraints of its physical infrastructure. So far, virtualisation has been a continuous evolution, from the first virtual machines (VMs) to the world of hybrid cloud, and there is no sign yet of this evolution losing momentum.
